Question
Given the root of a binary tree, return the length of the longest consecutive sequence path**.
A consecutive sequence path is a path where the values increase by one along the path.
Note that the path can start at any node in the tree, and you cannot go from a node to its parent in the path.
Example 1:
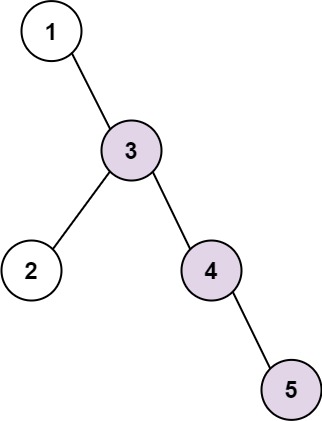
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,null,null,5]
Output: 3
Explanation: Longest consecutive sequence path is 3-4-5, so return 3.
Example 2:
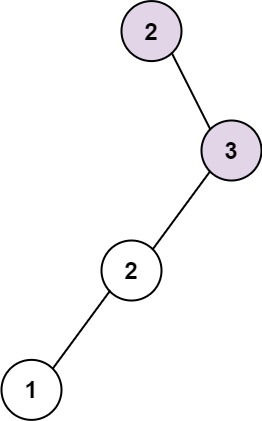
Input: root = [2,null,3,2,null,1]
Output: 2
Explanation: Longest consecutive sequence path is 2-3, not 3-2-1, so return 2.
Algorithm
Another typical binary tree question. Using preorder traversal, we calculate the max length each time we reach a new node until we reach the leaf nodes.
Code
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { int res = 0; public int longestConsecutive(TreeNode root) { helper(root, 1); return res; } private void helper(TreeNode root, int cur) { if (root == null) return; res = Math.max(cur, res); if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { return; } if (root.left != null) { if (root.left.val == root.val + 1) { helper(root.left, cur + 1); } else { helper(root.left, 1); } } if (root.right != null) { if (root.right.val == root.val + 1) { helper(root.right, cur + 1); } else { helper(root.right, 1); } } } }